Top AI Achievements of 2023
Uncover the transformative AI achievements of 2023, with a focus on NLP, computer vision, robotics, voice recognition, and HCI. This comprehensive overview highlights the latest advancements and their far-reaching impacts on technology, industry, and society.

AI achievements in 2023 were quite phenomenal. This year wasn't only a year of incremental progress; it was a year of breakthroughs. AI achievements in 2023 redefined what Artificial Intelligence could accomplish. From advancements in machine learning algorithms to developing more sophisticated robots, AI completely changes how we look around and live our lives.
The impact of these AI achievements in 2023 is far-reaching. Imagine a future where machines can understand and respond to complex human inquiries with impressive nuance, translate languages with remarkable accuracy, or even generate creative text formats on demand. These are just a glimpse of the exciting possibilities that emerged from AI's progress in 2023. This lurch signifies a future where AI can play a more prominent role in various aspects of our lives, potentially streamlining tasks, enhancing communication, and even aiding scientific discovery. As AI continues to evolve, we should utilize every beneficial aspect, keeping ethical considerations in mind.
In this article, we'll explore the fascinating world of AI by diving into five major fields: Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision (CV), Speech Recognition (SR), Robotics, and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). We'll look at the specific achievements within these fields and understand their significance. So, read and discover why 2023 is such a remarkable year for AI.

1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in 2023
NLP, or Natural Language Processing, teaches machines to understand and interact with human language. From translating languages to summarizing texts and even chatting with bots, NLP makes our interactions with technology smoother and more intuitive.
Before proceeding, here is something worth mentioning. All the LLMs that we use today would not be possible without a groundbreaking concept called “Transformer.”
Transformers are a type of deep learning model developed by Google. They rely on a technique called "multi-head attention" to process information. This technique was first introduced in a research paper titled "Attention Is All You Need" in 2017.
Here's how transformers work:
- Text to Numbers: The transformer first converts text into a series of numbers called "tokens." Each token represents a word or piece of text.
- Word Embeddings: These tokens are converted into vectors using a unique "word embedding table." This table basically assigns a unique numerical code to each word.
- Understanding Context: The core magic happens next. The transformer uses a process called "multi-head attention" to understand the context of each token. This means it considers the relationships between each token and other relevant tokens in the text. It essentially focuses on important tokens and downplays less important ones.
- Building on Attention: It's important to note that transformers build upon earlier research. The "softmax-based attention mechanism" used for machine translation in 2014 by Bahdanau and co-workers and the "Fast Weight Controller" concept from 1992 share similarities with the multi-head attention approach.
Bert, GPT-3, XLNet, and T5 are all based on transformer architecture.
OpenAI's ChatGPT-4
Wouldn't it be great to have a companion who would, in addition to submitting your questions, also be willing to return with a punchline? That is the description of ChatGPT-4, an LLM by OpenAI introduced at the end of 2023. This was not a minor change but a giant leap to how machines can understand and interpret human language and respond. The older language models can be better explained as simple suggestions software. You enter a search, and they come up with basic suggestions. It is different for ChatGPT-4; it works like a highly intelligent friend one can talk to.
Here's what makes ChatGPT-4 such a game-changer:
- Massive Dataset Training: Compared to the previous versions, ChatGPT-4 uses an enormous amount of text and code data. Comprising such a large training dataset gives it a vaster wordlist to work with and a better way of handling text in the natural setting. Thus, it can maintain more natural-like interaction and even grasp jokes and sarcasm (on occasion!).
- 1.76 trillion Parameter Power: In ML models like ChatGPT, a parameter is another tunable value that the model learns from data. It assists the model in fitting the data and determining the predictions it is to make. Think about that old dial on the radio: parameters are like those dials, allowing the fine-tuning of how ChatGPT interprets and generates information.
Imagine a computer program where increased processing power translates to better results. That's the case with ChatGPT-4. It is not confirmed officially, but ChatGPT-4 is believed to have 1.76 trillion parameters, which essentially act like tiny switches that help the model learn and make connections. This allows it to process information more complexly and generate more creative text formats, like poems, code snippets, or even scripts.
- Increased Input and Output Limits: Do you ever feel irritated by the chat tools only available for sending text messages? ChatGPT-4 shatters those limitations. It can now accept much longer input strings, and the resulting code produces much longer output strings. This made it possible to ask intricate questions and got elaborate answers as a result. Think about how one can have a philosophical discussion or write a whole blog post using ChatGPT-4.
The impact of ChatGPT-4 is huge. It has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with computers. Imagine automated customer service backed by LLMs that can truly understand your problems and offer helpful solutions. Or think about writers who can leverage ChatGPT-4 to brainstorm the ideas or write full-length blog post in few seconds. It's still early days, but one thing's for sure: ChatGPT-4 is a major step forward in AI, particularly the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). Its ability to communicate with humans in a natural and engaging way creates the possibility that we shall have our own Jarvis (Ironman’s AI).
Google AI's Gemini
We explored the impressive capabilities of ChatGPT-4, but AI achievements in 2023 extend beyond just one model. Google AI unveiled its powerhouse: Gemini. Think of Gemini as a Swiss Army knife in the world of AI, a single model that tackles various tasks with impressive competence.
Here's where Gemini shines:
- Code Comprehension Champion: Although ChatGPT-4 is oriented towards natural language, Gemini stands out for its code comprehension and Codegen capabilities. It would be amazing to have a tool that can not only write simple codes but also review them and diagnose errors. This could revolutionize programming by saving time and effort among programmers.
- Multimodal Master: While the former, ChatGPT-4, works with text inputs, Gemini has powerful multimodal features. This means that it can analyze text, images, and audio and provide a response in kind. Just think about being able to ask your AI assistant a question about a picture you took or translate the last conversation you had into text in real time.
- Efficiency Expert: One criticism of some of the largest models is that they are computationally expensive. To run them, one needs powerful computers. However, Gemini is more efficient as it is designed to operate with high efficiency. This means it can potentially be used on a wider range of devices, making its power more accessible.
Here are only several of the advantages of Gemini to give you a glimpse of what makes this company so great. Once again, like with ChatGPT-4, the full specifics of its features are not yet publicly disclosed. However, one thing is clear: both models are remarkable steps up for artificial intelligence in what machines are now capable of performing. With the advancement of AI, it would be interesting to know how these platforms, such as Gemini and ChatGPT-4, will influence the future of technologies and how they would assist in improving productivity in day-to-day operations.

Computer Vision (CV) in 2023
Computer Vision is another phenomenal subdivision of AI that allows machines to analyze and comprehend the visual data of the environment surrounding them. Uses of Computer Vision include image identification and segmentation, self-driving drones and cars, and medical diagnosis.
Let’s have a look at what achievements are made in the field of Computer Vision.
Deci AI's YOLO-NAS
Deci is excited to announce YOLO-NAS, a new object detection model built on the success of previous YOLO models, but it tackles their weaknesses. For example, some older YOLO models can't be easily converted to run on different devices. YOLO-NAS is built to be flexible and work well on various hardware.
Deci accomplished this with their AI-based NAS solution, AutoNAC. Therefore, it would be logical to consider AutoNAC a special tool that can be used to design unique, customized models. To clarify, you specify to AutoNAC what sort of object detection task you want to complete, and it forms a model that is as precise as it is fast and custom to your needs.
This is a big deal because a one-size-fits-all model doesn't exist. You wouldn't use the same model to analyze a live video stream on a tiny phone as you would to analyze high-resolution images on a powerful computer. AutoNAC helps bridge this gap.
Deci is even providing the YOLO-NAS model for free so people can modify it and see how things are done. They also have a knowledge base known as SuperGradients that simplifies training and deployment of YOLO-NAS.
Overall, YOLO-NAS represents a significant step forward in object detection. It's faster, more accurate, and more adaptable than previous models. This could be a game-changer for anyone working in computer vision.
AWS Panorama Device
AWS recently released the Panorama device, which will be a game-changer in edge computing for the CV. The Panorama device is designed to enable the real-time processing of the video stream at the device level, thus minimizing the necessity of uploading all the data to the cloud for further analysis.
It is specifically useful in fields such as retail since the Panorama device can determine consumer traffic, plan store navigation, and even control inventory levels in real-time. The ability to analyze data in a local environment can support decisions and actions in real-time, thereby improving organizational effectiveness.
Meta AI's DINOv2
Think about keeping top of a reinforcement learning approach where a computer vision model is trained with many unstructured images from the internet as if training a child to read with picture books. Here is the main concept of Meta AI’s brand-new DINOv2 tool.
DINOv2 is a big deal since the model performs substantially well without requiring excessive labeled data since they are costly to obtain. Remember when reading was easier than watching, when text was more informative than images? Labeled data could be described as picture books with captions. whereas unlabeled data means one can learn a lot by simply looking at the pictures.
Here's the cool part: In other words, DINOv2 can be applied as the base for most of the computer vision tasks. Well, let me tell you – one trains one model and then uses it to start with several tasks such as image classification, which involves the completion of recognizing the objects themselves in the given pictures, or depth estimation, which involves an understanding of how far objects are located from the camera. It’s like giving your artificial intelligence child a good start like when you introduce your child to school where they easily learn.
Apparently, DINOv2 can address issues that other methods encounter as well. For instance, some systems utilize captions to relate and identify images and can overlook some features. It is an interesting model because it learns directly from the images, which makes it perfect for some tasks, such as depth estimation.
DINOv2 is an open-source, so you can tinker with it and see how it works! Meta AI also collaborates with organizations like the World Resources Institute to use DINOv2 for real-world tasks like mapping forests. Pretty cool, right?
If you're interested in self-supervised learning and building powerful computer vision models, DINOv2 is worth checking out!
Cornell's Silent Speech Recognition
Cornell University researchers have developed a new wearable interface called EchoSpeech that allows for silent speech recognition. This technology can be a valuable tool for people who cannot vocalize sound or for situations where speaking aloud is inconvenient.
EchoSpeech analyzes lip movements using inaudible sound waves and microphones. It can be run on a smartphone and requires only a few minutes of user training data.
Here are some of the key benefits of EchoSpeech:
- Hands-free communication: EchoSpeech can be used to communicate with others via smartphone in places where speaking is difficult, such as noisy restaurants or libraries.
- Improved accessibility: For people who cannot speak, EchoSpeech could be used to control voice synthesizers.
- Privacy-focused: Because EchoSpeech uses sound waves instead of cameras, it offers greater privacy for users.
- Long battery life: EchoSpeech can last for up to 10 hours on a single charge, compared to just 30 minutes for camera-based systems.
The researchers are excited about the potential of EchoSpeech and are exploring ways to commercialize the technology. They are also looking into developing smart glass applications that use EchoSpeech to track facial movements.
Speech Recognition (SR) in 2023
Speech Recognition technology has advanced greatly, allowing machines to convert spoken language into text and understand it. This technology powers voice assistants, voice search, and automatic transcription services.
Development of AntiFake
One of the standout achievements in SR this year is the development of AntiFake technology. AntiFake is designed to detect deep fakes and synthetic speech, ensuring the authenticity of voice communications.
With the rise of deepfake technology, the ability to identify and prevent synthetic speech manipulation is crucial. AntiFake can be used in various fields, from securing online transactions to protecting public figures from voice impersonation, thereby enhancing trust and security in voice-based interactions.
DIverse yet Realistic Facial Animations (DIRFA)
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore developed an innovative AI program called DIRFA. This program can take a simple audio clip and a single photo and transform them into a remarkably realistic, 3D-animated video. The video goes beyond just lip-syncing; it includes natural head movements and a wide range of facial expressions that match the speaker's emotions.
To achieve this feat, DIRFA analyzes speech patterns and tones in the audio. By doing so, it can predict the corresponding facial expressions that a person would naturally make while speaking. This is a significant improvement over previous technologies, which often struggled to capture the subtleties of human emotion or handle variations in head pose.
DIRFA's training involved a massive dataset containing over one million audiovisual clips from over 6,000 people. This vast amount of data allowed DIRFA to learn the intricate connections between speech patterns and facial expressions. DIRFA has the potential to revolutionize multimedia communication by creating highly realistic videos. Some potential applications include:
- Communication Aids: A powerful tool for people with speech or facial disabilities to communicate through expressive avatars.
- Entertainment Industry: DIRFA could be used to create more realistic and expressive characters in animation, gaming, and virtual reality experiences. Imagine video game characters with lifelike facial responses during conversations or movie special effects with even more nuanced emotional portrayals.
- Education and Training: DIRFA could enhance educational materials and simulations by incorporating realistic facial expressions and body language from instructors or virtual characters. This could improve student engagement and understanding of complex topics.
- Video Conferencing and Social Media: DIRFA could be integrated into video conferencing platforms to create more natural and engaging interactions. It could also be used on social media platforms to allow users to express themselves more fully through avatars that mimic their facial expressions.
- Customer Service: Customer service chatbots could be equipped with DIRFA to provide more natural and empathetic customer interactions. This could improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Legal Proceedings: DIRFA could be used to create realistic reenactments of events from audio recordings, which could be helpful in legal proceedings.
DIRFA is still under development, and it has limitations such as the inability to fine-tune specific expressions. The researchers plan to improve DIRFA by incorporating a wider range of datasets and giving users more control over the output.
Robotics (ROB) in 2023
Robotics is a physical manifestation of artificial intelligence. In robotics, we can see machines following their training to perform certain tasks and constantly striving to achieve human-like robots capable of making decisions and performing tasks.
Here are some noteworthy achievements in the field of Robotics during the year 2023:
UBC Engineers' Breakthrough Robot Skin
This year, engineers at the University of British Columbia (UBC), in collaboration with Honda, developed a breakthrough robot skin. This new skin is capable of tactile sensing and adaptability, providing robots with a more human-like sense of touch through its smart, stretchable and highly sensitive soft sensor.
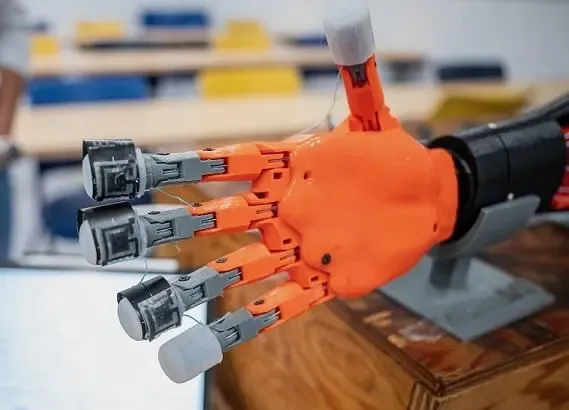
This advancement opens up numerous possibilities, such as robots that can perform delicate tasks like handling soft fruits without damaging them or providing enhanced feedback in prosthetics, making artificial limbs more responsive and intuitive for users. We hope that robots can feel pain in the near future as well.
Soft Robotic Hand by MIT
The Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT has made strides in developing a soft robotic hand. This hand is designed to mimic human dexterity, allowing it to grasp and manipulate objects with precision.
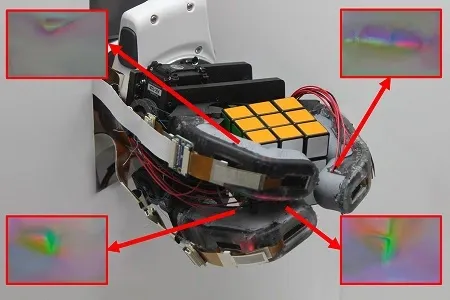
The soft robotic hand can be used in various fields, from industrial automation to assistive technologies for individuals with disabilities. Its ability to easily perform intricate tasks makes it a significant step forward in robotics. Surprisingly, the sensor is easy to manufacture and suitable for mass production, covering a larger skin area economically.
MIT's Camera-Based Touch Sensor
MIT researchers have also developed a long, curved, and finger-shaped camera-based touch sensor. This sensor provides high-resolution tactile sensing, enhancing robots' ability to interact with their environment.

The sensor's design allows it to be integrated into robotic systems for tasks that require precise manipulation and interaction, such as assembling small electronic components or performing delicate surgical procedures.
Mercedes-Benz achieved Level-3 Certification limited to Nevada
In early 2023, Mercedes-Benz announced receiving the first Level 3 certification in the United States, restricted to the designated highways within Nevada. This means their Drive Pilot system can handle certain driving tasks like steering, acceleration, and braking within its operational conditions. It also monitors driver attention through a camera in the car. If the driver doesn't respond to prompts to take control, Drive Pilot will bring the car to a safe stop. It's important to remember that Level 3 requires drivers to be ready to take control when prompted by the system.
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) in 2023
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) focuses on improving how humans interact with computers, making these interactions more intuitive and effective.
FDA gave green signal to Neuralink for Human trials
In a groundbreaking move for the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Neuralink received the green light from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2023 to begin human trials for their brain-computer interface (BCI) technology. This FDA approval marks a significant milestone, not just for Neuralink, but for the future of HCI as a whole.
Traditionally, HCI has focused on interactions through keyboards, mice, touchscreens, and even voice commands. However, Neuralink's BCI takes a revolutionary step by establishing a direct communication pathway between the brain and a computer. This bypasses traditional interfaces altogether, allowing users to control external devices or software with their thoughts.
The potential applications of Neuralink's technology within HCI are vast. Imagine a world where people with paralysis can regain control over limbs or prosthetic devices using their brainwaves. This could restore independence and improve the quality of life for millions. Additionally, BCI technology could offer new communication channels for individuals with speech or language difficulties.
The FDA approval signifies a crucial step towards realizing these possibilities. It validates the safety and initial efficacy of Neuralink's BCI design, allowing researchers to proceed with human trials named "Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface" (PRIME). This trial will involve implanting the BCI device in participants with paralysis and evaluating its ability to restore motor function and control external systems.
While the PRIME trial represents a crucial first step, it's important to remember that Neuralink's technology is still under development. Human trials will likely take time to complete, and widespread adoption of BCIs for everyday use is probably years away.
However, the FDA's approval in 2023 serves as a major milestone in the field of HCI. It opens doors for a future where our thoughts can directly interact with computers, blurring the lines between humans and machines in a way never before imagined. This achievement paves the way for a new era of HCI, pushing the boundaries of how we interact with technology and potentially transforming the lives of millions.
Robotic Glove for Stroke Rehabilitation
Stroke victims often struggle to play the piano again due to weakened hands and coordination issues. Existing robotic gloves are too stiff for delicate tasks like playing music. Researchers at Florida Atlantic University have created a new solution: a soft robotic glove with AI. This glove uses sensors to "feel" the difference between correct and wrong notes, offering real-time feedback and gentle assistance to improve finger movements.

Made from soft and flexible materials, the glove can be customized for each user. The AI analyzes sensor data to identify mistakes, and the glove then guides the user's fingers for proper playing. This technology has the potential to help stroke survivors regain the ability to play the piano and offers promise for other rehabilitation exercises. Doctors can use the data to personalize therapy plans, creating a more customized path to recovery for patients with limited hand function.
Future Directions in HCI
Looking ahead, HCI is poised to continue evolving, with trends like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) playing a significant role. As we integrate more natural and immersive ways to interact with technology, the line between human and machine will blur, making our interactions more seamless and intuitive.
Final Thoughts
2023 has been a year of remarkable progress in the field of AI, with significant advancements across Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Speech Recognition, Robotics, Human-Computer Interaction and others as well. These achievements highlight the incredible potential of AI to transform our world, making it more intelligent, efficient, and connected. As we look to the future, the possibilities for AI are endless, and the journey has only just begun.



